Feb 28, 2025
The global economy is facing a rapidly increasing level of uncertainty, including the impact of the trade policies of the Trump administration in the U.S., as a result of the change of government in many countries. The main scenario is that growth will continue at around 3% between 2025 and 2026, based on the assumption that the endless escalation of trade wars will be avoided. However, the main risks are (1) the expansion of the impact of the Trump administration's policy of prioritizing the interests of the U.S., (2) financial market turmoil accompanying a resurgence of inflation in the U.S., and (3) the economic downturn in China and the escalation of social unrest and the problem of excessive exports. In addition, developments towards a ceasefire in the wars in Ukraine and the Middle East, and the tight supply and demand situation for energy due to the rapid expansion of demand for data centers and responses to this, are thought to have both positive and negative impacts on the economy. The global growth rate is expected to be 3.2% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026.
The U.S. economy is maintaining a strong performance. The Trump administration's pro-business deregulation and policies strongly encouraging investment in the U.S. are expected to improve business sentiment and boost the economy. On the other hand, if tariffs are imposed on a wide range of goods, such as automobiles, it could gradually depress the domestic economy through increased household burdens. Due to strong demand, inflation is expected to remain high, and the Federal Reserve is likely to keep its policy rate unchanged in 2025. The risks for 2025 include the resurgence of inflation in the U.S. and financial market turmoil, such as a sharp drop in stock prices due to Fed interest rate hikes. The real GDP growth rate is expected to be 2.4% in 2025 and 1.8% in 2026.
The euro area economy continues to experience a slowdown. In the October-December 2024 period, both Germany and France saw negative growth. Political instability in both countries has increased policy uncertainty, which is suppressing domestic demand. In 2025, if the U.S. imposes tariffs, it could lower exports to the U.S., but an increase in defense spending is expected to support the economy. The ECB is expected to keep its policy interest rate unchanged after reducing it to 2%. In the UK, manufacturing sentiment has worsened, and the BOE is expected to implement continued interest rate cuts. The real GDP growth rate for the euro area is projected to be 0.9% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026. For the UK, the real GDP growth rate is expected to be 1.0% in 2025 and 1.4% in 2026.
The Chinese economy is stagnating due to the limited effectiveness and sustainability of stimulus measures. Exports are expected to decrease compared to 2024, despite an increase in exports to ASEAN and the Middle East and in detouring exports due to the imposition of additional 10% tariffs by the U.S. Manufacturing and infrastructure investment will remain strong thanks to the government's expanded support measures, but direct investment from overseas, including Japanese companies, will continue to decline. Real estate prices are on a recovery trend in major cities, but will continue to fall in rural areas. Consumption is expected to see a recovery due to the effects of the government's replacement promotion measures, but due to the slump in consumer sentiment caused by asset deflation and employment insecurity, a significant recovery is unlikely. The real GDP growth rate is expected to be 4.4% in 2025 and 4.2% in 2026.
The Japanese economy in 2025 is expected to experience a gradual recovery, supported by strong inbound demand, DX and GX initiatives, and capital investment driven by high corporate profitability. However, consumption recovery will be delayed until the second half of the year due to prolonged high inflation exceeding initial expectations. Exports will be driven by demand from Asian markets excluding China, but downside risks remain, particularly for exports to the U.S. and China. The Bank of Japan is expected to implement an additional 0.25% rate hike in 2025. The Japanese economy is projected to recover, with real GDP growth rates forecasted at 1.6% for 2025 (1.2% for FY) and 1.1% for 2026 (1.3% for FY).
In India, inflation has stabilized and the central bank has decided to cut interest rates in consideration of the economy. While there is concern about import inflation due to the depreciation of the rupee, it is expected that in addition to financial support, fiscal policies such as income tax cuts will be implemented, and high growth is expected to be maintained at 6.4% in FY2025 and 6.3% in FY2026. The ASEAN5 are also expected to continue to enjoy stable growth, but they may be affected by the impact of U.S. trade policy and trends in the Chinese economy. Some countries, such as Vietnam, which have large trade surpluses with the U.S., will need to pay particular attention to the Trump administration's trade policy. The growth rate for the ASEAN5 is likely to be 5.0% in both 2025 and 2026.
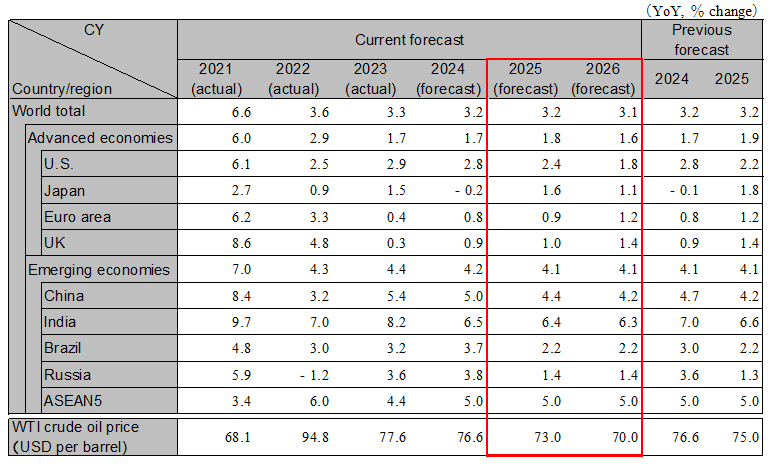
Note: Values for Japan differ from those shown in the table below on a fiscal-year basis because they are on a calendar-year basis. However, India’s figures are shown on a fiscal-year basis. ASEAN5 is comprised of Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
Source: Actual figures are from the IMF, forecasts are from the IMF (Brazil and Russia), and Hitachi Research Institute (others)
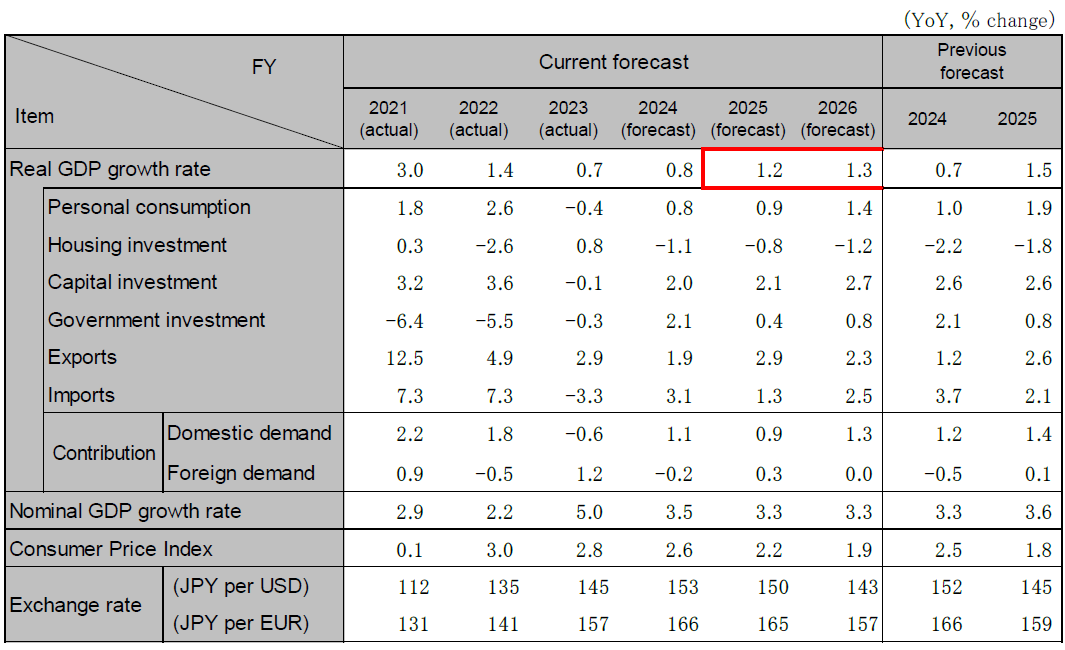
Note: The individual numbers and their sum may not match due to fractional processing.
Source: Cabinet Office, forecasts by Hitachi Research Institute
We provide you with the latest information on HRI‘s periodicals, such as our journal and economic forecasts, as well as reports, interviews, columns, and other information based on our research activities.
Hitachi Research Institute welcomes questions, consultations, and inquiries related to articles published in the "Hitachi Souken" Journal through our contact form.